Val-cit-PAB-OH / 100 mg
Safety Information
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Pictograms
Properties
| Signal Word | Warning |
Product Description
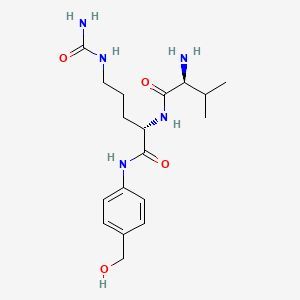
Val-cit-PAB-OH is a synthetic prodrug designed for targeted delivery of cytotoxic agents in cancer therapy. It consists of valine, citrulline, and p-aminobenzoic acid linked together, forming a molecule that can be selectively taken up by certain types of cancer cells. Upon entering these cells, Val-cit-PAB-OH undergoes metabolic activation to release the active cytotoxic component, which then targets and kills the cancer cells. This targeted approach aims to minimize damage to healthy tissues, potentially improving patient outcomes and reducing side effects associated with conventional chemotherapy.
Application
In clinical settings, Val-cit-PAB-OH is being explored as part of novel strategies in cancer treatment, particularly for solid tumors that overexpress specific transporters. Its use in combination therapies could enhance the efficacy of existing treatments by delivering higher concentrations of cytotoxic agents directly to tumor sites. Research into Val-cit-PAB-OH is ongoing, focusing on optimizing its formulation and delivery mechanisms to maximize its therapeutic potential.
Articles:
- Protease-Mediated Fragmentation of p-Amidobenzyl Ethers: A New Strategy for the Activation of Anticancer Prodrugs
Publication Date: February 12, 2002
Brian E. Toki, Charles G. Cerveny, Alan F. Wahl, and Peter D. Senter
https://doi.org/10.1021/jo016187+
- Systematic Variation of Pyrrolobenzodiazepine (PBD)-Dimer Payload Physicochemical Properties Impacts Efficacy and Tolerability of the Corresponding Antibody–Drug Conjugates
Publication Date: July 31, 2020
Leanna R. Staben, Jinhua Chen, Josefa dela Cruz-Chuh, Geoff del Rosario, Mary Ann Go, Jun Guo, S. Cyrus Khojasteh, Katherine R. Kozak, Guangmin Li, Carl Ng, Gail D. Lewis Phillips, Thomas H. Pillow, Rebecca K. Rowntree, John Wai, BinQing Wei, Keyang Xu, Zijin Xu, Shang-Fan Yu, Donglu Zhang, and Peter S. Dragovich
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c00691
- Targeting conserved N-glycosylation blocks SARS-CoV-2 variant infection in vitro
Publication Date: November 25, 2021
Hsiang-Chi Huang, Yun-Ju Lai, Chun-Che Liao, Feng-Yang Wang, Ke-Bin Huang, I-Jung Lee, Wen-Cheng Chou, Shih-Han Wang, Ling-Hui Wang, Jung-Mao Hsu, Cheng-Pu Sun, Chun-Tse Kuo, Jyun Wang, Tzu-Chun Hsiao, Po-Jiun Yang, Te-An Lee, Wilson Huang, Fu-An Li, Chen-Yang Shen, Yi-Ling Lin, Mi-Hua Tao, Chia-Wei Li